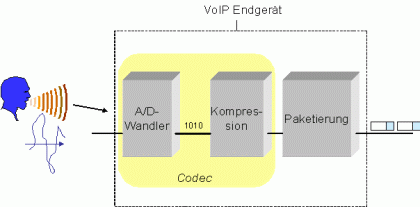
A codec (Coder/Decoder) converts analog signals to a digital bitstream, and another identical codec at the far end of the communication converts the digital bitstream back into an analog signal.
In the VoIP world, codecs are used to encode voice for transmission across IP networks.
Codecs for VoIP use are also referred to as vocoders, for “voice encoders”.
Codecs generally provide a compression capability to save network bandwidth. Some codecs also support silence suppression, where silence is not encoded or transmitted.
| Codec | Algorithm | Bit Rate (Kbps) | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|
| ITU G.711 | PCM (Pulse Code Modulation) | 64 | G.711 with mu-law used in North America and Japan, while G.711 with A-law used in the rest of the world. |
| ITU G.722 | SBADPCM (Sub-Band Adaptive Differential Pulse Code Modulation) | 48, 56 and 64 | |
| ITU G.723 | Multi-rate Coder | 5.3 and 6.4 | |
| ITU G.726 | ADPCM (Adaptive Differential Pulse Code Modulation) | 16, 24, 32, and 40 | |
| ITU G.727 | Variable-Rate ADPCM | 16-40 | |
| ITU G.728 | LD-CELP (Low-Delay Code Excited Linear Prediction) | 16 | |
| ITU G.729 | CS-ACELP (Conjugate Structure Algebraic-Code Excited Linear Prediction) | 8 | |
| ILBC | Internet Low Bitrate Codec | 13.33 and 15.20 | |
| Speex | CELP (Code Excited Linear Prediction) | 2.15-44.2 | Part of the GNU Project and available under the Xiph.org variant of the BSD license |
| GSM – Full Rate | RPE-LTP (Regular Pulse Excitation Long-Term Prediction) | 13 | |
| GSM – Enhanced Full Rate | ACELP (Algebraic Code Excited Linear Prediction) | 12.2 | |
| GSM – Half Rate | CELP-VSELP (Code Excited Linear Prediction – Vector Sum Excited Linear Prediction) | 11.4 | |
| DoD FS-1016 | CELP (Code Excited Linear Prediction) | 4.8 |




babu
where codecs located? in Voip phones or call manager or gateway. can you explain please…….