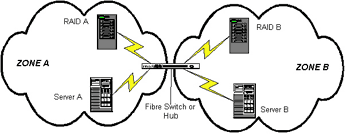
SAN zoning is a method of arranging Fibre Channel devices into logical groups over the physical configuration of the fabric.
SAN zoning may be utilized to implement compartmentalization of data for security purposes.
Each device in a SAN may be placed into multiple zones.
Hard and Soft Zoning
Hard zoning is zoning which is implemented in hardware. Soft zoning is zoning which is implemented in software.
Hard zoning physically blocks access to a zone from any device outside of the zone.
Soft zoning uses filtering implemented in fibre channel switches to prevent ports from being seen from outside of their assigned zones. The security vulnerability in soft zoning is that the ports are still accessible if the user in another zone correctly guesses the fibre channel address.
WWN Zoning
WWN zoning uses name servers in the switches to either allow or block access to particular World Wide Names (WWNs) in the fabric.
A major advantage of WWN zoning is the ability to recable the fabric without having to redo the zone information.
WWN zoning is susceptible to unauthorized access, as the zone can be bypassed if an attacker is able to spoof the World Wide Name of an authorized HBA.
Port Zoning
Port zoning utilizes physical ports to define security zones. A users access to data is determined by what physical port he or she is connected to.
With port zoning, zone information must be updated every time a user changes switch ports. In addition, port zoning does not allow zones to overlap.
Port zoning is normally implemented using hard zoning, but could also be implemented using soft zoning.



Follow Us!