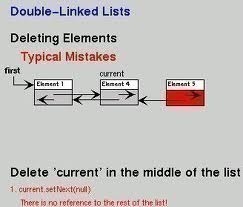
To delete an element from the list, first the pointers are set properly and then the memory occupied by the node to be deleted is deallocated (freed).
Deletion in the list can take place at the following positions.
- At the beginning of the list
- At the end of the list
- After a given element
- Before a given element
Deleting from the Beginning of the List
An element from the beginning of the list can be deleted by performing the following steps:
- Assign the value of head (address of the first element of the list) to a temporary variable (say temp)
- There are two further cases:
- Deallocate the memory occupied by the node pointed to by temp.
C Code
.cf { font-family: Lucida Console; font-size: 9pt; color: black; background: white; }
.cl { margin: 0px; }
.cb1 { color: green; }
.cb2 { color: blue; }
.cb3 { color: maroon; }
void deletefrombeginning( node **head, node **tail)
{
node *temp;
if(*head==NULL)
return;
temp=*head;
if(*head==*tail) /*one element only*/
*head=*tail=NULL;
else
{
(temp->next)->prev=NULL;
*head=temp->next;
}
free(temp);
}
Deleting from the End of the List
An element from the end of the list can be deleted by performing the following steps:
- Assign the value of tail (address of the last element of the list) to a temporary variable (say temp)
- Further there are two cases:
- If there is only one element in the existing list, set both head and tail to NULL.
- If there is more than one element in the list then
- Assign NULL to the next pointer field of the second last node.
- Assign the address of the second last node to tail.
- Deallocate the memory occupied by the node pointed to by temp.
C Code
void deletefromend( node **head, node **tail)
{
node *temp;
if(*head==NULL)
return;
temp=*tail;
if(*head==*tail) /*one element only*/
*head=*tail=NULL;
else
{
temp->prev->next=NULL;
*tail=temp->prev;
nbsp; }
free(temp);
}
Deleting after a Given Element
void deleteafterelement (node **head, node **tail, int after)
{
node *temp, *loc;
temp = *head;
loc = search(temp,after);
if (loc == NULL) /*search item not found*/
return;
temp = loc->next;
loc->next = temp->next;
if(temp->next == NULL)
*tail = loc;
else
(temp->next)->prev = loc;
free(temp);
}
Deleting before a Given Element
void deletebeforeelement (node **head, int before)
{
node *temp, *loc;
temp=*head;
loc=search(temp,before);
if(loc==NULL)
return;
temp=loc->prev;
loc->prev=temp->prev;
if(temp->prev==NULL)
*head=loc;
else
(temp->prev)->next=loc;
free(temp);
}
Freeing up the Entire List
The doubly linked list can be deleted either from the beginning or from the end. To delete from the beginning, use the following steps:
- Assign the head pointer to a temporary variable, say temp.
- Advance the head pointer to the next node.
- Deallocate the memory occupied by the node pointed to by temp.
Repeat the above steps until the entire list is deleted. Finally, set the tail pointer to NULL.
C Code
void deletelist(node **head, node **tail)
{
node *temp;
while(*head!=NULL)
{
temp=*head;
*head=(*head)->next;
free(temp);
}
*tail=NULL;
}



Follow Us!