The Frequency-Hopping Spread Spectrum (FHSS) is a means of transmitting radio signals by shifting a carrier across a number of channels with a pseudorandom sequence that the sending and receiving station knows beforehand. The method is used as a multiple access process in the FH-CDMA (Frequency Hopping Code Division Multiple Access) transmission scheme.
What Are the Advantages of Spread-Spectrum Transmission?
The frequency hopping spread spectrum over a fixed-frequency transmission method has 3 primary advantages:
#1 – The method is very resistant to narrow band interference since the spread signal causes the interfering signal to recede into the background.
#2 – The signals are very difficult to intercept. FHSS signals make it seem like there has been an increase in background noise when a narrow band receiver detects them. In order to intercept the signal, the pseudorandom transmission hopping sequence has to be known.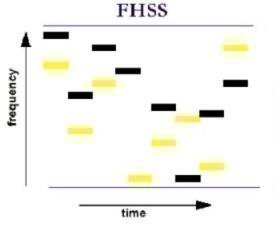
#3 – FHSS transmissions can share frequency bands with a number of other types of conventional transmissions without causing significant interference. Each of these signals causes minimal interference and allows the bandwidth to be used more effectively.
What is the Basic Frequency Hopping Spread Spectrum Algorithm?
The basic algorithm for successfully transmitting and receiving an FHSS signal is:
Step 1 – The calling/initiating party sends a request via a control channel or other pre-defined frequency.
Step 2 – The receiving party then sends a seed number back to the initiating party.
Step 3 – The seed number is then used as the key variable in the pre-defined algorithm for the FHSS communications device, that then calculates the series of frequencies to use during the communication session. Many times, this period of frequency change is pre-defined so that a single base station can service a number of communication connections.
Step 4 – The calling/initiating party then sends a synchronization signal on the first frequency in the calculated sequence.
Step 5 – The communication session between the two parties commences and each party shifts frequencies in sync with the other.
When the military uses this communications method, cryptographic techniques that encrypt communications and generate the channel sequence to be used during the communications session are utilized. Two U.S. Military radios that use this method are the HAVEQUICK and SINCGARS radios.
What Are the Challenges of Frequency Hopping Spread Spectrum Technology?
Spread-spectrum communications need greater bandwidth than when only a single carrier frequency is used. Also, one of the most problematic aspects of the technology is to initially synchronize the transmitter and receiver. Although most issues can be worked through, a significant amount of time must be initially allotted to learning this process.
Who Invented Frequency Hopping?
Several persons are credited with inventing frequency hopping. The first was Johannes Zenneck (in 1908), a German who is on the record for stating that his company, Telefunken had already invented the technology. Later, Polish inventor, Leonard Danilewicz developed the idea separately. Actress Hedy Lamarr and George Antheil received a U.S. patent on a frequency hopping technology that used 88 frequencies.



Follow Us!