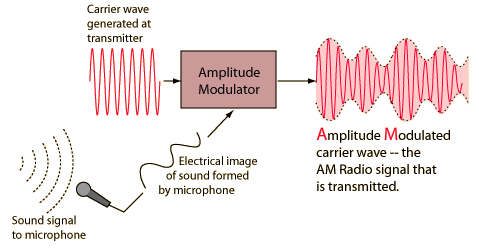
How Speakers Blow
A speaker is a device that converts electrical signals into actual sound. Speakers accomplish this by using a magnetic reader or antenna to receive an electrical signal from a radio station or magnetic storage device. The magnetic reader is then connected via a wire to an electromagnet that can be turned on and off in …