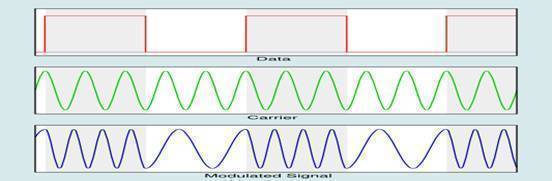
FSK (Frequency Shift Keying)
FSK (Frequency Shift Keying) is also known as frequency shift modulation and frequency shift signaling. Frequency Shift Keying is a data signal converted into a specific frequency or tone in order to transmit it over wire, cable, optical fiber or wireless media to a destination point. The history of FSK dates back to the early …