192.168.1.1 – What Are its Uses and Why is it Important?
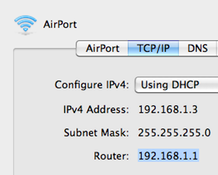
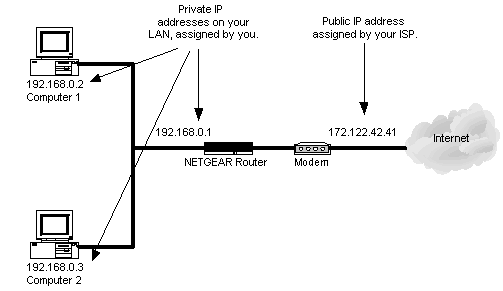
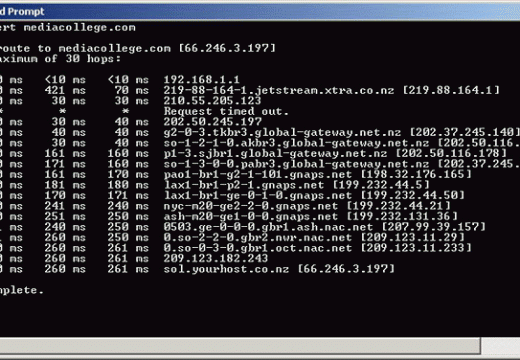
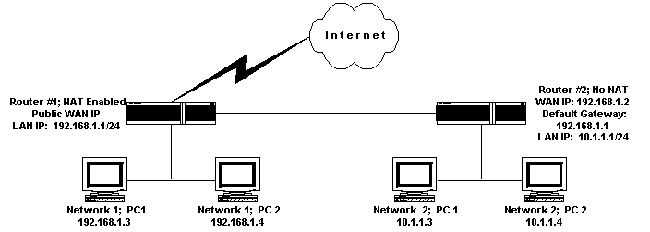
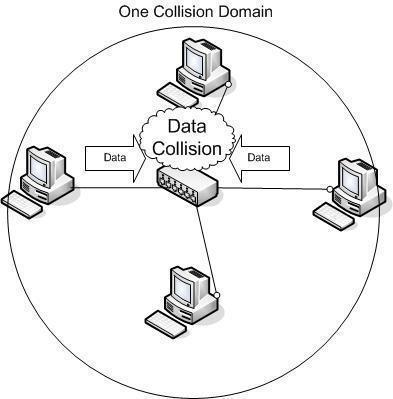
The 192.168.1.1 IP address is a default commonly used by Linksys routers. Linksys is now a division of Cisco, Incorporated and makes a large number of the broadband routers used throughout the world. The address is not exclusive to Linksys, but most other major router manufacturers use different default addresses for configuration of home or …