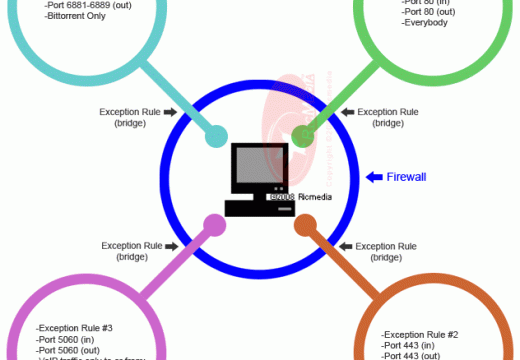
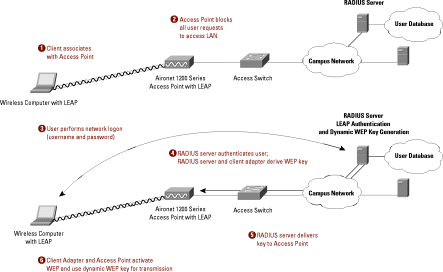
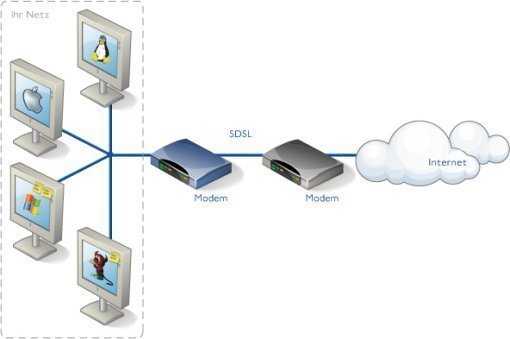
Firewalls
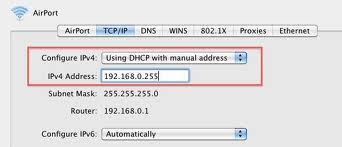
A firewall is a software component that restricts unauthorized inward network access. It allows outward information flow. It is set up to control traffic flow between two networks by configured permissions like Allow, Deny, Block, Encrypt, etc. It is normally employed to avoid illegal access to personal computers or corporate networks from external unsafe entities …