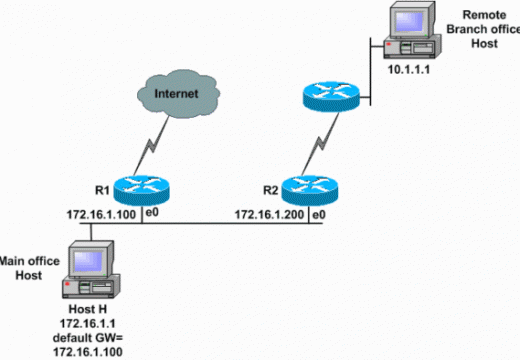
Broadband over Power Lines
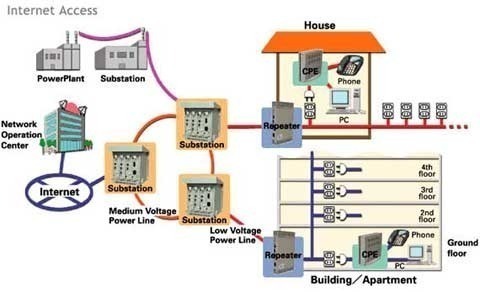
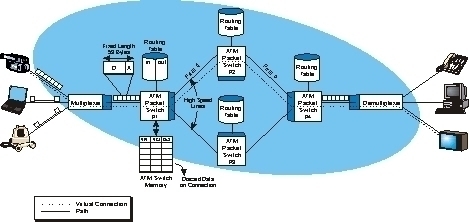
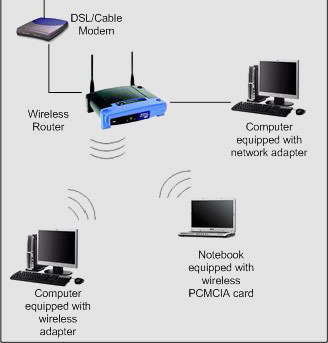
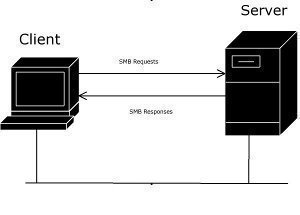
Broadband over Power Lines, or BPL, refers to the transmission (sending and receiving) of digital data through existing power cables and electricity distribution infrastructures. This can be viewed as a mere variation on using television cables; instead of using television cables, though, power transmission lines are going to be used. The Broadband over Power Lines …