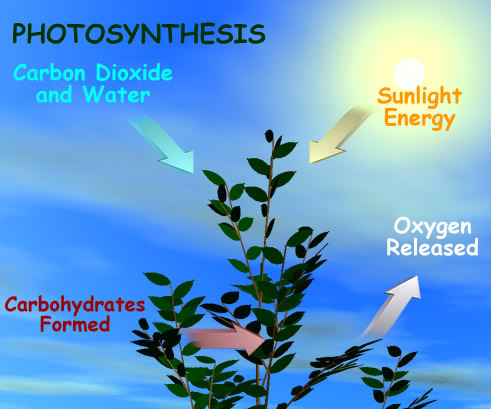
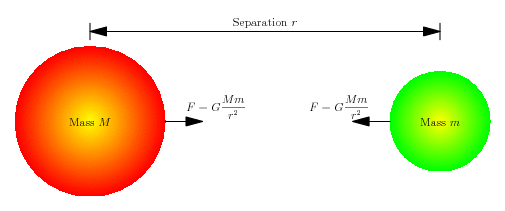
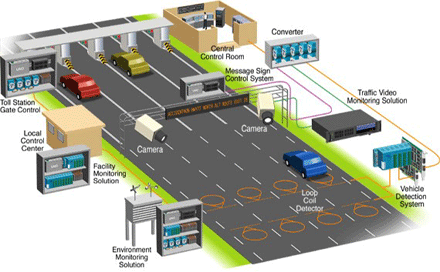
Driverless Cars
A driverless car (also autonomous/autopilot/auto-drive car) refers to a car that does not need human intervention to function. The first driverless car achieved a maximum speed of 20 miles-per-hour and was built by Tsukuba Mechanical Engineering Laboratory in 1977. The Mercedes Benz robot van built during the 1980s achieved a full speed of 60 miles-per-hour …