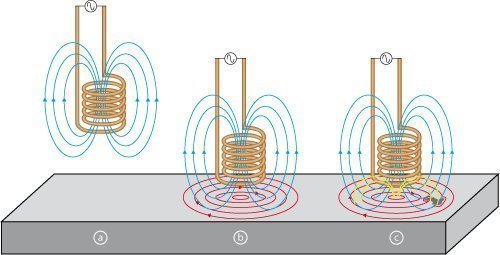
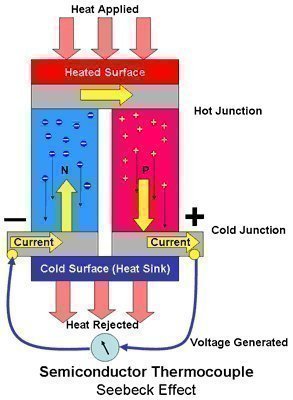
Weather Modification Technology
Weather modification refers to willful manipulation of the climate or local weather. Research done in this field goes back to as far as the early 1940s when the US military experimented with cloud seeding to stimulate rain. Today, private corporations have joined the weather modification research effort to protect people, cities and assets from the …