Substitution and Transposition Ciphers
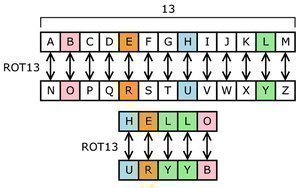
Substitution and transposition ciphers are two categories of ciphers used in classical cryptography. Substitution and transposition differ in how chunks of the message are handled by the encryption process. Substitution ciphers Substitution ciphers encrypt plaintext by changing the plaintext one piece at a time. The Caesar Cipher was an early substitution cipher. In the Caesar …