The application layer of a software is a protocol that is used for communication between a software and the network layers that it uses. The application layer allows a computer’s network to interpret requests made by the program and allows the program to interpret data from the network. Likewise, the application layer ensures that both parties are available and can communicate with another, authenticates messages from both parties, and ensures that both parties agree about privacy, data integrity, and error recovery.
How An Application Layer Works
The application layer is one of seven protocols in the OSI (Open Systems Interconnection) Model that is activated before all other protocols, including the presentation layer, session layer, transport layer, network layer, data link layer, and physical link layer. The TCP/IP protocol also uses the application layer, which also includes the presentation layer and session layer. In both models, the application layer receives data from the user and performs a variety of maintenance checks before passing the information on to the layers beneath it.
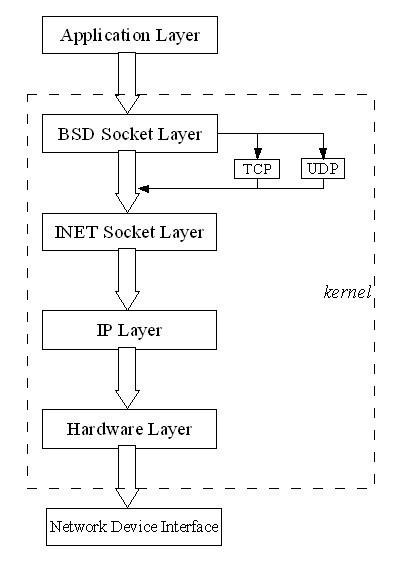
The application layer is used for a wide variety of applications, such as authentication, error checking, and redirection of data. The application layer is most notably used to retrieve files from other system resources when actions cannot be performed locally. For example, the HTTP protocol that is used in virtually all web browsers is used by the application layer to request files on third-party servers and networks and display them to the user.
Advantages
The application layer is advantageous because it allows applications to communicate with other network layers as well as other networks. The application layer is also advantageous because it runs in the background of the user’s computer and is never noticed unless the user specifically accesses application layer tools.

Follow Us!