A browser cookie is a small piece of information sent by a web server to a web browser to be stored for future use. The data in the browser cookie will be sent back to the web server whenever the browser reconnects to the web site.
Cookies are commonly used to store user preference information, such as web site options. Cookies are also used to store shopping cart contents. Cookies are also used to store authentication data, such as user names and passwords.
How Websites Use Cookies
Cookies are extremely small pieces of information (usually only a few bytes in size, no longer than 255 characters). Cookies make it easy to customize a site. For instance, if you visit a news site that requires members to register and then log in, a cookie can tell the news web site web server that you are already a registered member and that you no longer need to log in, which means you can easily access the site without any additional steps. Cookies are also used to track a users web habits. For instance, a web server can usually tell which pages the user is interested in.
What a Cookie is NOT
Cookies are not viruses, spyware, adware, or malware; they are extremely small programs that can only be read by the web server that created them.
It is important to note that cookies can not steal your personal information. A cookie can usually help the web server identify the visitor and match up the cookie to an IP address of your computer, the name of your computer, the browser that you are using, the operating system that you are using and the current URL page and previous URL page you have accessed.
Cookies and Advertising
Since a cookie is able to record the habits of a visitor on a specific web site, advertisers are always interested to know as much as possible about visitors and their on-site behavior. Collecting this information is easy with the help of cookies. Although your name and personal information are anonymous, your computer name and your web surfing habits on a specific site using a cookie are not. A web site can use the information about a user and offer these to visitors next time they visit the site. For instance, let’s say that you own a sports web site that caters to basketball, baseball and football. One visitor with the computer name John, visits the site each day, but only visits the web pages associated with baseball products. Knowing this information, you can offer this visitor products and services related only to baseball.
First-Party, Third-Party Cookies, and Session Cookies
First-Party Cookies are cookies from the web site you are surfing. Third-Party Cookies are cookies from other web sites that advertise on the web site you are surfing.
Common senders of Third-Party Cookies include L90.com, Advertising,com, Avenue A, Bfast.com, ClickAgents.com, DoubleClick.com, FastClick.com, Focalink, Mediaplex, Shopnow, Speedyclick, Uproad, and Valueclick.
Session cookies are cookies which are not stored on the browser’s computer. Session cookies are deleted when the user closes the browser. Because session cookies are not saved between sessions, they are seen as less of a security risk than permanent cookies.
How to Allow Cookies
Allow Cookies With Internet Explorer
To allow cookies with IE, go to the tools menu and then select Internet Options. This will open a new window that has a series of different tabs. Click the privacy button. Depending on the version of IE you’re using, this might be what you need to access cookies, but if not, click the Default button. Then, move the slider up and down. Close the Internet Options down and restart the browser.
Allow Cookies With Firefox
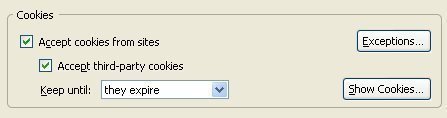
Go to tools and then hit the options button. Similar to Internet Explorer, click the privacy feature. Then click the cookies button. Expand it so you can see all of the different options in front of you. Check the “Enable Cookies” and “Accept cookies normally” check boxes. Then hit OK and restart the browser.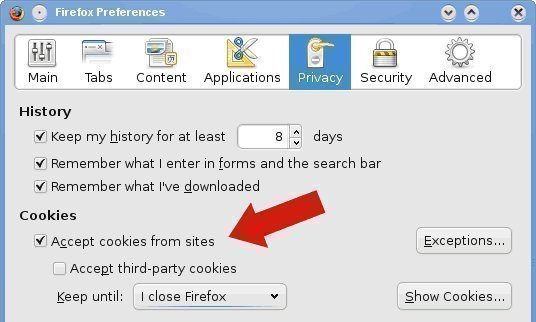
Allow Cookies With Opera
This is very similar to how it is done with Firefox. Go to tools and then select preferences. Go to privacy and then click enable cookies. This is the first check box. The next one to click is accept all cookies. Save the changes by hitting OK and then close the preferences down.
Allow Cookies With Safari
Go to tools and then preferences. Click security. Look for the Accept Cookies section. Underneath it, the “Always or Only from sites you navigate” feature should be checked. Hit OK to save your features and then go to the site you need cookies for. If you need to, reset the browser to ensure that the feature works.
How to Enable Cookies on Google Chrome
By default, Google Chrome allows all cookies from websites.
However, the user has complete control over giving cookies permission in Google Chrome and the settings can be adjusted by following these directions:
1. Click the “Wrench” icon on the browser toolbar.
2. Select Options (On Mac and Linux, Preferences. On a Chromebook, Settings).
3. Click the Under the Hood tab.
4. Click Content settings in the “Privacy” section.
5. Click the Cookies tab in the “Content Settings” dialog that appears.
Managing Cookie Settings
From this screen, there are several options for managing cookies in Google Chrome.
Google Chrome can be set to block all cookies (or only third party cookies) by default, allow all cookies by default, or only allow cookies from sites on the exceptions list. The user can also delete all cookies from this screen.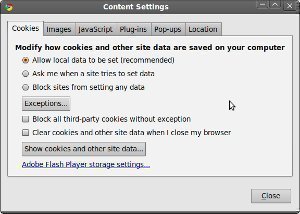
- To delete cookies, select All cookies and site data to open a dialog box.
- To remove all cookies, select Remove all at the bottom of the dialog.
- To delete a specific cookie, select the site that issued the cookie from the list and click Remove.
All cookies from a specific time period can also be deleted with the “Clear Browsing Data” dialog.
Google Chrome can also be set to delete all cookies whenever the browser is closed, or to delete cookies from specific sites everytime the browser is closed. This setting can be changed with the “Clear cookies and other site data when I close my browser” checkbox in the “Content Settings” dialog.
- To set Google Chrome to block all cookies by default, select “Block sites from setting any data.”
It is important to know that most sites that require a user to sign in will be non-operational if this box is checked.
- To allow cookies in Google Chrome, select “Allow local data to be set.”
- To manage how cookies are handled for a specific site, click “Manage exceptions.”
- To add a new exception in the dialog that appears, click the “Add a new exception pattern” field and enter the domain name.
- Exceptions for an entire domain can be can be made by inserting [*.] before the domain name. An example would be [*.]tech-faq.com.
Disabling Cookies
Most web browsers can be configured to alert the user when a cookie is sent, or even to refuse cookies altogether. Refusing to send cookies will make some web sites more difficult to use and will make some web sites unusable.
How To Disable Cookies in Internet Explorer
To set the cookie handling options in SlimBrowser or Internet Explorer, select the Tools menu and then the Internet Options menu item. From there, select the Privacy tab and click the Advanced button. Check Override automatic cookie handling and you will be given access to a new set of menu options.
You are given the option to Accept, Block, or Prompt on First-Party Cookies and Third-Party Cookies.
How To Disable Cookies in Netscape Navigator
To set the cookie handling options in Netscape Navigator, select the Edit menu and then the Preferences menu item. From there, double-click the Privacy and Security item from the left menu to open up the Privacy and Security menu items. Next, select the Cookies submenu to display your options.
You are given options to:
- Disable cookies
- Enable cookies for the originating web site only (i.e. enable first-party cookies and disable third-party cookies)
- Enable cookies based on privacy settings (this option allows you to enable cookies based upon the web sites published privacy policy)
- Enable all cookies
You are also given options to:
- Disable cookies in Mail and Newsgroups
- Ask me before storing a cookie
- Limit maximum lifetime of cookies
You can also click the Managed Stored Cookies button. This will show you the cookies currently stored by Netscape Navigator and allow you to selectively delete cookies. This menu will also allow you to disable or enable cookies for specific web sites.
How To Disable Cookies in Opera
To set the cookie handling options in Opera, select the File menu and then the Preferences menu item. From there, click the Privacy item from the left menu.
In the Cookies section on the right, you are given the option to:
- Enable cookies
Next you are given options for displaying or automatically accepting cookies:
- Do not accept cookies
- Display received cookies
- Accept only cookies from selected servers
- Automatically accept all cookies
You are then given options for enabling first-party and third-party cookies:
- Accept from all servers
- Do not accept third party cookies
- Display third party cookies
- Accept from all servers
Finally, you are given options to:
- Throw away new cookies on exit
- Display warning for illegal domains
- Accept illegal path
- Display warning for illegal path
How to Disable Cookies In Firefox
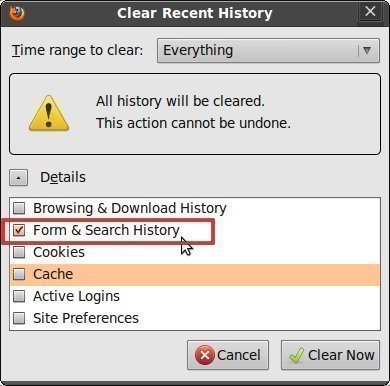
In Mozilla Firefox, you can disable cookies by unchecking these boxes or selecting a different option in the drop down menu under the History section such as “Remember history” or “Never remember history” and clicking the OK button again.



Follow Us!