CSMA/CD (Carrier Sense Multiple Access / Collision Detection) is the protocol used in Ethernet networks to ensure that only one network node is transmitting on the network wire at any one time.
Carrier Sense means that every Ethernet device listens to the Ethernet wire before it attempts to transmit. If the Ethernet device senses that another device is transmitting, it will wait to transmit.
Multiple Access means that more than one Ethernet device can be sensing (listening and waiting to transmit) at a time.
Collision Detection means that when multiple Ethernet devices accidentally transmit at the same time, they are able to detect this error.
How Collisions Occur under CSMA/CD
Imagine a very simple Ethernet network with only two nodes.
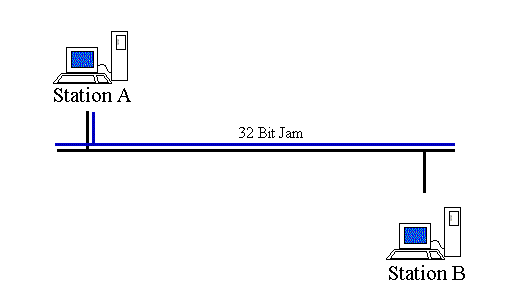
Each node independently decides to send an Ethernet frame to the other node.
Both nodes listen to the Ethernet wire and sense that no carrier is present.
Both nodes transmit simultaneously, causing a collision.
Both nodes detect the collision and each node waits a random amount of time before transmitting again.
Collisions are normal on an Ethernet network. A small amount of collisions are expected in the protocol design.
If too many nodes are transmitting on an Ethernet network, the number of collisions can rise to an unacceptable level. This can reduce the amount of available bandwidth on an Ethernet network because so much bandwidth is lost in retransmission.
Ethernet switches greatly reduce the already minor difficulties experienced with the CSMA/CD protocol.



Zahid
Please tell me how a node listens to the medium that its free or not? or take it as ..how a node detects a carrier on the ethernet wire ? Please reply soon.
aanchal
i also need more information……
prateek
great
but i need more deeply information
Mukesh Joshi
The explanation was in very simple words but was very good.
Thanks
matacha
unless CSMA/CA, CSMA/CD sends signals after collision had occured. What are other differences?
saikrishnan
thanks…
that was quite easy to understand !
kd & Ph
thanks dude good explanation
samuel
good but differentiate with cs ma/ca
Andy
Thanxx…a lot it was easy to understand!!!!
arindam bhattacharjee
Thanx a lot for sharing
amit
it is very simple explain
subardhan
good explanation , very helpful thanks…..
Murugesh_CIT_India
good but further more detail is required… for ex: how does the station listens to the channel and how does it know the channel is busy or used… and what kind of jamming error is woken
Dhaval Vithalani
it is really too helpfool…Thanks a lot..
Suvadip
its really helpful man, thanks a lot. 😆 😆 😆
Tan Cong
It’s really good. Thanks 🙂
Dang Nguyen
great, thanks! 😉
shakil
I understood it clearly. Thank u for the explanation.
jason polydor
Its a simple explanation, very instructive. thanks