A PRI (Primary Rate Interface) is a telecommunication standard used in the Integrated Services Digital Network or ISDN for carrying multiple DS0 voice and data transmissions between two physical locations. PRI was developed specifically for industrial or large quantity users. It is an industrial ISDN line, while the Basic Rate Interface, or BRI, caters to home and small enterprises.
Both Primary Rate Interface and Basic Rate Interface are made up of a number of B channels and D channels. The B Channel (Bearer Channel) is used for data transmission, including voice, and the D channel is meant for signaling and control. A PRI is made up of 23 B-channels, one 64 Kbps D-channel in a T-1 configuration, 30 B-channels, and 1 D-channel using an E1 line.
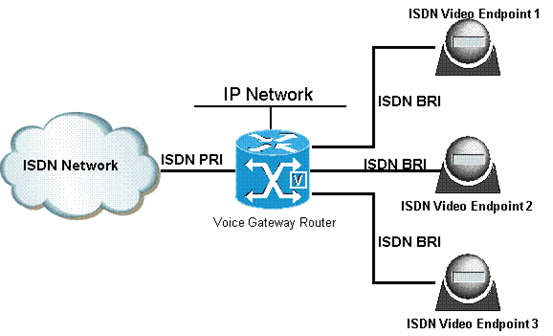
The T-carrier system is standard in Japan, US, and Canada, while E1 is popular across Europe and Australia. In other words, in North America and Japan, PRI is represented as 23B+D with a total bit rate of 1.544 Mbit/s (T1), while it is 30B+D in Australia and Europe, which is equivalent to a bit rate of 2.048 Mbit/s (E1). The Primary Rate Interface uses the Q.931 protocol over the D channel.
A PRI is typically used to establish communication between a PBX (private branch exchange), which is a telephone exchange that a telephone company’s customer operates, and the telephone company’s Central Office or an Inter Exchange Carrier or IXC, a long distance telephone company. The PRI’s (primary rate interface) advantage is that the 23 or 30 B channels can be used in various combinations for specific data transmission needs such as videoconferencing, allowing bulk data transfer to be achieved more flexibly.


Follow Us!