ISO 7816 is the internationally accepted standard for smart cards. ISO 7816 is a family of standards primarily dealing with aspects of smart card interoperability regarding communication characteristics, physical properties, and application identifiers of the implanted chip and data.
The ISO 7816 family includes eleven parts which are in a constant state of flux as they are subject to revision and update. ANSI can be contacted to get the latest version of the 7816 standards.
ISO 7816 Standards
ISO 7816-1
The ISO 7816-1 standard specifies the physical characteristics of the card. Physical characteristics of a card includes: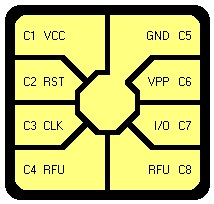
- Dimensions
- Electromagnetic radiation
- Mechanical stress
- Location of integrated IC in card
- Location of the magnetic strip
- Resistance to static electricity
ISO 7816-2
The ISO 7816-2 standard defines the location of contacts and dimensions. It also defines the purpose, location and electrical characteristics of the metallic contacts of the card.
ISO 7816-3
The ISO 7816-3 standard is designed to deal with electronic signals and transmission protocols.
ISO 7816-3 specifies the current and voltage requirements for the electrical contacts which are:
- Asynchronous half-duplex character transmission protocol (T=0).
- Asynchronous half duplex block transmission protocol (T=1). Smart cards that use a proprietary transmission protocol carry the designation with it.
- T=14 includes revision of protocol type selection.
ISO 7816-4
The ISO 7816-4 standard defines the inter-industry interchange commands for the card’s CPU. It provides the facility of interoperability across all industries to provide security and transmission of card data. It defines the basic commands for reading, writing and updating of card data.
ISO 7816-5
The ISO 7816-5 standard deals with registration procedure for Application Identifiers (AID) and the Numbering System. It defines the standards for Application Identifiers which has two parts:
- Registered Application Provider Identifier (RID) of five bytes that is unique to the vendor.
- A variable length field of up to 11 bytes that RIDs can use to identify specific applications.
ISO 7816-6
The ISO 7816-5 standard defines the physical transfer of device and operational data. Two transmission protocols are included in it: character protocol (T=0) or block protocol (T=1). A card may support either but not both simultaneously. If the card is not following any of the standards then it is treated as (T=14)
ISO 7816-7
Structured Card Query Language (SCQL) is given for the inter-industry interoperability of commands for Structured Card Query Language (SCQL). It specifies the standard method to maintain and query the database, it also provides format definitions.
ISO 7816-8
Security operation commands are standardized by this criterion. ISO 7861-8 includes the commands for internal security management of the card and may include encryption techniques and other security management methods.
ISO 7816-9
The ISO 7816-9 standard includes specifications for the commands for card management. The following provides the primary interests of this standard:
- Description and coding of security attributes of card related objects
- Functions and syntax of additional inter-industry commands
- Description and coding of the life cycle of cards and related objects
- Data elements associated with these commands
- Mechanism for initiating card-originated messages
ISO 7816-10
The ISO 7816-10 standard is designed to address electrical signals and reset signals for synchronous cards. It includes the following:
- Signal structures
- Power
- Structure for the reset signal which is sent between the card IC and the interface device such as a terminal
ISO 7816-11
The ISO 7816-11 standard is meant for personal identification of the user. It ay use biometric methods and standards to achieve personal identification.
Other Relevant Industry Standards
Apart from the above standards, some industry specific standards are also generally followed. Some of those industry standards are as follows:
- IC Communications Standards
- HIPAA – The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act adopts national standards for implementing a secure electronic health transaction system
- EMV – Europay, MasterCard and Visa formed EMV Company, LLC and created the “Integrated Circuit Card Specifications for Payment Systems”
- CEN (Comite’ Europe’en de Normalisation) and ETSI (European Telecommunications Standards Institute) is focused on telecommunications, as with the GSM SIM for cellular telephones.
- FIPS (Federal Information Processing Standards) was developed by the Computer Security Division within National Institute of Standards and Technology. FIPS standards are designed to protect federal assets including computer and telecommunications systems.




Follow Us!