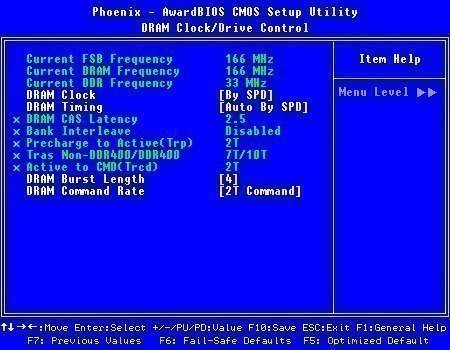
CAS latency is short for Column Address Strobe latency.
CAS latency is the time (in clock cycles) required to access a column of memory on a DRAM memory module.
A CAS3 rated memory module requires 3 clock cycles to address a column of memory, where a CAS2 rated memory module can accomplish the same task in only two clock cycles.
Three steps are required to address DRAM on a memory module, such as a DIMM:
- Memory bank selection
- Memory row selection (Row Address Strobe)
- Memory column selection (Column Address Strobe)
CAS latency is sometimes abbreviated as CL.



Follow Us!