Ethernet is the most common LAN (Local Area Network) technology in use today. Xerox developed Ethernet in the 1970s, and became popular after Digital Equipment Corporation and Intel joined Xerox in developing the Ethernet standard in 1980. Ethernet was officially accepted as IEEE standard 802.3 in 1985. The term “Ethernet” is now used to refer to all derivatives of the original Xerox “Ethernet”.
Ethernet Speeds
The original Xerox Ethernet operated at 3Mbps. Ethernet became popular as a 10Mbps standard over coaxial or twisted pair cabling. Fast Ethernet improved speeds to 100Mbps over twisted pair or fiber optic cables. Gigabit Ethernet now provides speeds up to 1Gpbs over twister pair or fiber optic cabling.
Ethernet Cabling
The first Ethernet standard, 10Base-5, ran over thick coaxial cable. A later standard, Ethernet 10Base-2, ran over a much thinner coaxial cable. These two versions of Ethernet were colloquially known as thicknet and thinnet.

Modern Ethernet standards run on UTP (Unshielded Twisted Pair) or fiber-optic cabling.
| Ethernet Standard | Cable Specification |
|---|---|
| 10Base-T | Category 3 UTP |
| 100Base-TX | Category 5 UTP |
| 1000Base-T | Cat 5e UTP |
| 1000Base-SX | Optical Fiber |
Ethernet Topologies
Ethernet 10Base-5 and 10Base-2 used a bus topology. Bus topologies were difficult to maintain and troubleshoot.
Modern Ethernet networks use a star topology with an Ethernet hub, switch, or router at the center of the star.
It is still possible to create a two-node Ethernet network in a bus topology using a null-Ethernet cable between the two devices.
Ethernet DTE and DCE
All nodes on an Ethernet network are either DTE (Data Terminal Equipment) or DCE (Data Communications Equipment).
Ethernet DTE are devices such as computers and printers that are trying to communicate on the Ethernet network.
Ethernet DCE are devices such as switches and routers that are trying to help other devices communicate on the Ethernet network.
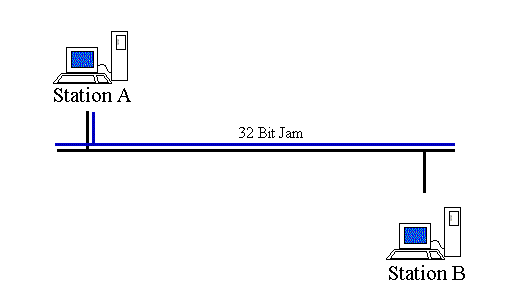
Ethernet CSMA/CD
Like any network, Ethernet must have an algorithm for determining when each network node is allowed to communicate.
In Ethernet, this algorithm is known as CSMA/CD (Carrier Sense Multiple Access / Collision Detection).
CSMA/CD has proven to be a very capable, if highly anarchistic, algorithm.
Related Articles on Ethernet Technology
- What is Ethernet?
- Understanding Ethernet
- Ethernet at the Data Link Layer
- Ethernet at Physical Layer
- Understanding Ethernet Networking
- Understanding Ethernet LAN Segmentation
- What is an Ethernet Card?
- What is an Ethernet Hub?
- What is an Ethernet Switch?
- Ethernet Cable
- Ethernet Cabling
- What Is the Ethernet Cable Pinout?
- What is a USB to Ethernet adapter?
- What is Power over Ethernet?
- What is an Ethernet crossover cable?
- Ethernet Cross Over Cable


Follow Us!