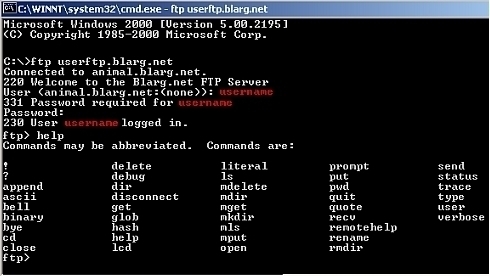
The usable FTP commands will differ from one FTP client to the next, but these are a set of fairly standard FTP commands as implemented in the FreeBSD FTP client.
- ! [command [args]]
- Invoke an interactive shell on the local machine. If there are arguments, the first is taken to be a command to execute directly, with the rest of the arguments as its arguments.
- $ macro-name [args]
- Execute the macro macro-name that was defined with the macdef command. Arguments are passed to the macro unglobbed.
- account [passwd]
-
Supply a supplemental password required by a remote system for access to resources once a login has been successfully completed. If no argument is included, the user will be prompted for an account password in a non-echoing input mode.
- append local-file [remote-file]
- Append a local file to a file on the remote machine. If remote-file is left unspecified, the local file name is used in naming the remote file after being altered by any ntrans or nmap setting. File transfer uses the current settings for type, format, mode, and structure.
- ascii
- Set the file transfer type to network ASCII. This is the default type.
- bell
- Arrange that a bell be sounded after each file transfer command is completed.
- binary
- Set the file transfer type to support binary image transfer.
- bye
- Terminate the FTP session with the remote server and exit ftp. An end of file will also terminate the session and exit.
- case
- Toggle remote computer file name case mapping during get, mget and mput commands. When case is on (default is off), remote computer file names with all letters in upper case are written in the local directory with the letters mapped to lower case.
- cd remote-directory
- Change the working directory on the remote machine to remote-directory.
- cdup
- Change the remote machine working directory to the parent of the current remote machine working directory.
- chmod mode remote-file
- Change the permission modes of the file remote-file on the remote system to mode.
- close
- Terminate the FTP session with the remote server, and return to the command interpreter. Any defined macros are erased.
- cr
- Toggle carriage return stripping during ascii type file retrieval. Records are denoted by a carriage return/linefeed sequence during ascii type file transfer. When cr is on (the default), carriage returns are stripped from this sequence to conform with the Unix single linefeed record delimiter. Records on non-UNIX remote systems may contain single linefeeds; when an ascii type transfer is made, these linefeeds may be distinguished from a record delimiter only when cr is off.
- debug [debug-value]
Toggle debugging mode. If an optional debug-value is specified it is used to set the debugging level. When debugging is on, ftp prints each command sent to the remote machine, preceded by the string `–>'
- delete remote-file
- Delete the file remote-file on the remote machine.
- dir [remote-path [local-file]]
- Print a listing of the contents of a directory on the remote machine. The listing includes any system-dependent information that the server chooses to include; for example, most Unix systems will produce output from the command `ls -l'. If remote-path is left unspecified, the current working directory is used. If interactive prompting is on, ftp will prompt the user to verify that the last argument is indeed the target local file for receiving dir output. If no local file is specified, or if local-file is `-', the output is sent to the terminal.
- disconnect
- A synonym for close.
- edit
- Toggle command line editing, and context sensitive command and file completion. This is automatically enabled if input is from a terminal, and disabled otherwise.
- epsv4
- Toggle the use of the extended EPSV and EPRT commands on IPv4 connections; first try EPSV / EPRT, and then PASV / PORT. This is enabled by default. If an extended command fails then this option will be temporarily disabled for the duration of the current connection, or until epsv4 is executed again.
- exit
- A synonym for bye.
- features
- Display what features the remote server supports (using the FEAT command).
- fget localfile
- Retrieve the files listed in localfile, which has one line per filename.
- form format
- Set the file transfer form to format. The default (and only supported) format is “non-print''.
- ftp host [port]
- A synonym for open.
- gate [host [port]]
- Toggle gate-ftp mode, which used to connect through the TIS FWTK and Gauntlet ftp proxies. This will not be permitted if the gate-ftp server hasn't been set (either explicitly by the user, or from the FTPSERVER environment variable). If host is given, then gate-ftp mode will be enabled, and the gate-ftp server will be set to host. If port is also given, that will be used as the port to connect to on the gate-ftp server.
- get remote-file [local-file]
- Retrieve the remote-file and store it on the local machine. If the local file name is not specified, it is given the same name it has on the remote machine, subject to alteration by the current case, ntrans, and nmap settings. The current settings for type, form, mode, and structure are used while transferring the file.
- glob
- Toggle filename expansion for mdelete, mget, mput, and mreget. If globbing is turned off with glob, the file name arguments are taken literally and not expanded. Globbing for mput is done as in csh. For mdelete, mget, and mreget, each remote file name is expanded separately on the remote machine and the lists are not merged. Expansion of a directory name is likely to be different from expansion of the name of an ordinary file: the exact result depends on the foreign operating system and ftp server, and can be previewed by doing `mls remote-files -' Note: mget, mput and mreget are not meant to transfer entire directory subtrees of files. That can be done by transferring a tar archive of the subtree (in binary mode).
- hash [size]
- Toggle hash-sign (“#'') printing for each data block transferred. The size of a data block defaults to 1024 bytes. This can be changed by specifying size in bytes. Enabling hash disables progress.
- help [command]
- Print an informative message about the meaning of command. If no argument is given, ftp prints a list of the known commands.
- idle [seconds]
- Set the inactivity timer on the remote server to seconds seconds. If seconds is omitted, the current inactivity timer is printed.
- image
- A synonym for binary.
- lcd [directory]
- Change the working directory on the local machine. If no directory is specified, the user's home directory is used.
- less file
- A synonym for page.
- lpage local-file
- Display local-file with the program specified by the set pager option.
- lpwd
- Print the working directory on the local machine.
- ls [remote-path [local-file]]
- A synonym for dir.
- macdef macro-name
- Define a macro. Subsequent lines are stored as the macro macro-name; a null line (consecutive newline characters in a file or carriage returns from the terminal) terminates macro input mode. There is a limit of 16 macros and 4096 total characters in all defined macros. Macros remain defined until a close command is executed. The macro processor interprets `$' and `' as special characters. A `$' followed by a number (or numbers) is replaced by the corresponding argument on the macro invocation command line. A `$' followed by an `i' signals that macro processor that the executing macro is to be looped. On the first pass `$i' is replaced by the first argument on the macro invocation command line, on the second pass it is replaced by the second argument, and so on. A `' followed by any character is replaced by that character. Use the `' to prevent special treatment of the `$'.
- mdelete [remote-files]
- Delete the remote-files on the remote machine.

- mdir remote-files local-file
- Like dir, except multiple remote files may be specified. If interactive prompting is on, ftp will prompt the user to verify that the last argument is indeed the target local file for receiving mdir output.
- mget remote-files
- Expand the remote-files on the remote machine and do a get for each file name thus produced. See glob for details on the filename expansion. Resulting file names will then be processed according to case, ntrans, and nmap settings. Files are transferred into the local working directory, which can be changed with `lcd directory'; new local directories can be created with `! mkdir directory'.
- mkdir directory-name
- Make a directory on the remote machine.
- mls remote-files local-file
- Like ls, except multiple remote files may be specified, and the local-file must be specified. If interactive prompting is on, ftp will prompt the user to verify that the last argument is indeed the target local file for receiving mls output.
- mlsd [remote-path]
- Display the contents of remote-path (which should default to the current directory if not given) in a machine-parsable form, using MLSD. The format of display can be changed with `remopts mlst …'.
- mlst [remote-path]
- Display the details about remote-path (which should default to the current directory if not given) in a machine-parsable form, using MLST. The format of display can be changed with `remopts mlst …'.
- mode mode-name
- Set the file transfer mode to mode-name. The default (and only supported) mode is “stream''.
- modtime remote-file
- Show the last modification time of the file on the remote machine.
- more file
- A synonym for page.
- mput local-files
- Expand wild cards in the list of local files given as arguments and do a put for each file in the resulting list. See glob for details of filename expansion. Resulting file names will then be processed according to ntrans and nmap settings.
- mreget remote-files
- As per mget, but performs a reget instead of get.
- msend local-files
- A synonym for mput.
- newer remote-file [local-file]
- Get the file only if the modification time of the remote file is more recent that the file on the current system. If the file does not exist on the current system, the remote file is considered newer. Otherwise, this command is identical to get.
- nlist [remote-path [local-file]]
- A synonym for ls.
- nmap [inpattern outpattern]
-
Set or unset the filename mapping mechanism. If no arguments are specified, the filename mapping mechanism is unset. If arguments are specified, remote filenames are mapped during mput commands and put commands issued without a specified remote target filename. If arguments are specified, local filenames are mapped during mget commands and get commands issued without a specified local target filename. This command is useful when connecting to a non-UNIX remote computer with different file naming conventions or practices. The mapping follows the pattern set by inpattern and outpattern. [Inpattern] is a template for incoming filenames (which may have already been processed according to the ntrans and case settings). Variable templating is accomplished by including the sequences `$1', `$2', …, `$9' in inpattern. Use `' to prevent this special treatment of the `$' character. All other characters are treated literally, and are used to determine the nmap [inpattern] variable values. For example, given inpattern $1.$2 and the remote file name "mydata.data", $1 would have the value "mydata", and $2 would have the value "data". The outpattern determines the resulting mapped filename. The sequences `$1', `$2', …., `$9' are replaced by any value resulting from the inpattern template. The sequence `$0' is replace by the original filename. Additionally, the sequence `[seq1, seq2]' is replaced by [seq1] if seq1 is not a null string; otherwise it is replaced by seq2. For example, the command
nmap $1.$2.$3 [$1,$2].[$2,file]
would yield the output filename "myfile.data" for input filenames "myfile.data" and "myfile.data.old", "myfile.file" for the input filename "myfile", and "myfile.myfile" for the input filename ".myfile". Spaces may be included in outpattern, as in the example: `nmap $1 sed "s/ *$//" > $1' . Use the `' character to prevent special treatment of the `$','[',']', and `,' characters.
- ntrans [inchars [outchars]]
- Set or unset the filename character translation mechanism. If no arguments are specified, the filename character translation mechanism is unset. If arguments are specified, characters in remote filenames are translated during mput commands and put commands issued without a specified remote target filename. If arguments are specified, characters in local filenames are translated during mget commands and get commands issued without a specified local target filename. This command is useful when connecting to a non-UNIX remote computer with different file naming conventions or practices. Characters in a filename matching a character in inchars are replaced with the corresponding character in outchars. If the character's position in inchars is longer than the length of outchars, the character is deleted from the file name.
- open host [port]
- Establish a connection to the specified host FTP server. An optional port number may be supplied, in which case, ftp will attempt to contact an FTP server at that port. If the set auto-login option is on (default), ftp will also attempt to automatically log the user in to the FTP server.
- page file
- Retrieve file and display with the program specified by the set pager option.
- passive [auto]
- Toggle passive mode (if no arguments are given). If auto is given, act as if FTPMODE is set to `auto'. If passive mode is turned on (default), ftp will send a PASV command for all data connections instead of a PORT command. The PASV command requests that the remote server open a port for the data connection and return the address of that port. The remote server listens on that port and the client connects to it. When using the more traditional PORT command, the client listens on a port and sends that address to the remote server, who connects back to it. Passive mode is useful when using ftp through a gateway router or host that controls the directionality of traffic. (Note that though FTP servers are required to support the PASV command by RFC 1123, some do not.)
- pdir [remote-path]
- Perform dir [remote-path], and display the result with the program specified by the set pager option.
- pls [remote-path]
- Perform ls [remote-path], and display the result with the program specified by the set pager option.
- pmlsd [remote-path]
- Perform mlsd [remote-path], and display the result with the program specified by the set pager option.
- preserve
- Toggle preservation of modification times on retrieved files.
- progress
- Toggle display of transfer progress bar. The progress bar will be disabled for a transfer that has local-file as `-' or a command that starts with `|'. Refer to FILE NAMING CONVENTIONS for more information. Enabling progress disables hash.
- prompt
-
Toggle interactive prompting. Interactive prompting occurs during multiple file transfers to allow the user to selectively retrieve or store files. If prompting is turned off (default is on), any mget or mput will transfer all files, and any mdelete will delete all files. When prompting is on, the following commands are available at a prompt:
- a: Answer `yes' to the current file, and automatically answer `yes' to any remaining files for the current command.
- n: Answer `no', and do not transfer the file.
- p: Answer `yes' to the current file, and turn off prompt mode (as is “prompt off'' had been given).
- q: Terminate the current operation.
- y: Answer `yes', and transfer the file.
- ?: Display a help message.
Any other response will answer `yes' to the current file.
- proxy ftp-command
- Execute an ftp command on a secondary control connection. This command allows simultaneous connection to two remote FTP servers for transferring files between the two servers. The first proxy command should be an open, to establish the secondary control connection. Enter the command "proxy ?" to see other FTP commands executable on the secondary connection. The following commands behave differently when prefaced by proxy: open will not define new macros during the auto-login process, close will not erase existing macro definitions, get and mget transfer files from the host on the primary control connection to the host on the secondary control connection, and put, mput, and append transfer files from the host on the secondary control connection to the host on the primary control connection. Third party file transfers depend upon support of the FTP protocol PASV command by the server on the secondary control connection.
- put local-file [remote-file]
- Store a local file on the remote machine. If remote-file is left unspecified, the local file name is used after processing according to any ntrans or nmap settings in naming the remote file. File transfer uses the current settings for type, format, mode, and structure.
- pwd
- Print the name of the current working directory on the remote machine.
- quit
- A synonym for bye.
- quote arg1 arg2 …
- The arguments specified are sent, verbatim, to the remote FTP server.
- rate direction [maximum [increment]]
-
Throttle the maximum transfer rate to maximum bytes/second. If maximum is 0, disable the throttle. direction may be one of:
- all: Both directions
- get: Incoming transfers
- put: Outgoing transfers
maximum can be modified on the fly by increment bytes (default: 1024) each time a given signal is received:
- SIGUSR1: Increment maximum by increment bytes.
- SIGUSR2: Decrement maximum by increment bytes. The result must be a positive number.
If maximum is not supplied, the current throttle rates are displayed. Note: rate is not yet implemented for ascii mode transfers.
- rcvbuf size
- Set the size of the socket receive buffer to size.
- recv remote-file [local-file]
- A synonym for get.
- reget remote-file [local-file]
- reget acts like get, except that if local-file exists and is smaller than remote-file, local-file is presumed to be a partially transferred copy of remote-file and the transfer is continued from the apparent point of failure. This command is useful when transferring very large files over networks that are prone to dropping connections.
- remopts command [command-options]
- Set options on the remote FTP server for command to command-options (whose absence is handled on a command-specific basis). Remote FTP commands known to support options include: `MLST' (used for MLSD and MLST).
- rename [from [to]]
- Rename the file from on the remote machine, to the file to.
- reset
- Clear reply queue. This command re-synchronizes command/reply sequencing with the remote FTP server. Resynchronization may be necessary following a violation of the FTP protocol by the remote server
-
.

- restart marker
- Restart the immediately following get or put at the indicated marker. On Unix systems, marker is usually a byte offset into the file.
- rhelp [command-name]
- Request help from the remote FTP server. If a command-name is specified it is supplied to the server as well.
- rmdir directory-name
- Delete a directory on the remote machine.
- rstatus [remote-file]
- With no arguments, show status of remote machine. If remote-file is specified, show status of remote-file on remote machine.
- runique
- Toggle storing of files on the local system with unique filenames. If a file already exists with a name equal to the target local filename for a get or mget command, a ".1" is appended to the name. If the resulting name matches another existing file, a ".2" is appended to the original name. If this process continues up to ".99", an error message is printed, and the transfer does not take place. The generated unique filename will be reported. Note that runique will not affect local files generated from a shell command (see below). The default value is off.
- send local-file [remote-file]
- A synonym for put.
- sendport
- Toggle the use of PORT commands. By default, ftp will attempt to use a PORT command when establishing a connection for each data transfer. The use of PORT commands can prevent delays when performing multiple file transfers. If the PORT command fails, ftp will use the default data port. When the use of PORT commands is disabled, no attempt will be made to use PORT commands for each data transfer. This is useful for certain FTP implementations which do ignore PORT commands but, incorrectly, indicate they've been accepted.
- set [option value]
-
Set option to value. If option and value are not given, display all of the options and their values. The currently supported options are:
- anonpass: Defaults to $FTPANONPASS
- ftp_proxy: Defaults to $ftp_proxy.
- http_proxy: Defaults to $http_proxy.
- no_proxy: Defaults to $no_proxy.
- pager: Defaults to $PAGER.
- prompt: Defaults to $FTPPROMPT.
- rprompt: Defaults to $FTPRPROMPT.
- site arg1 arg2 …
- The arguments specified are sent, verbatim, to the remote FTP server as a SITE command.
- size remote-file
- Return size of remote-file on remote machine.
- sndbuf size
- Set the size of the socket send buffer to size.
- status
- Show the current status of ftp.
- struct struct-name
- Set the file transfer structure to struct-name. The default (and only supported) structure is “file''.
- sunique
- Toggle storing of files on remote machine under unique file names. The remote FTP server must support FTP protocol STOU command for successful completion. The remote server will report unique name. Default value is off.
- system
- Show the type of operating system running on the remote machine.
- tenex
- Set the file transfer type to that needed to talk to TENEX machines.
- throttle
- A synonym for rate.
- trace
- Toggle packet tracing.
- type [type-name]
- Set the file transfer type to type-name. If no type is specified, the current type is printed. The default type is network ASCII.
- umask [newmask]
- Set the default umask on the remote server to newmask. If newmask is omitted, the current umask is printed.
- unset option
- Unset option. Refer to set for more information.
- usage command
- Print the usage message for command.
- user user-name [password [account]]
- Identify yourself to the remote FTP server. If the password is not specified and the server requires it, ftp will prompt the user for it (after disabling local echo). If an account field is not specified, and the FTP server requires it, the user will be prompted for it. If an account field is specified, an account command will be relayed to the remote server after the login sequence is completed if the remote server did not require it for logging in. Unless ftp is invoked with “auto-login'' disabled, this process is done automatically on initial connection to the FTP server.
- verbose
- Toggle verbose mode. In verbose mode, all responses from the FTP server are displayed to the user. In addition, if verbose is on, when a file transfer completes, statistics regarding the efficiency of the transfer are reported. By default, verbose is on.
- xferbuf size
- Set the size of the socket send and receive buffers to size.
- ? [command]
- A synonym for help.

Follow Us!