IP address spoofing denotes the action of generating IP packets with fake source IP addresses in order to impersonate other systems or to protect the identity of the sender. Spoofing can also refer to forging or using fake headers on emails or netnews to – again – protect the identity of the sender and to mislead the receiver or the network as to the origin and validity of sent data.
Basics of IP Address Spoofing
The Internet Protocol or IP is the fundamental protocol for sending/receiving data over computer networks and the Internet. With the Internet protocol, each packet sent or received contains information relevant to the operation such as the source and the destination of the packet. With IP address spoofing, the information placed on the source field is not the actual source of the packet. By using a different address in the source field of the packet, the actual sender can make it look like the packet was sent by another computer and thus the response of the target computer will be sent to the fake address specified in the packet – unless the attacker wants to redirect the response to his own computer.
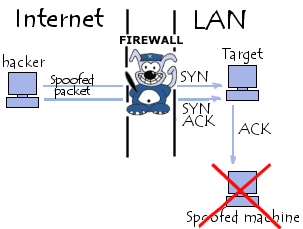
Effects of IP Address Spoofing
IP address spoofing is very useful especially in the case of denial of service (DoS) attacks where large amounts of information are sent to a target computer or system without the perpetrators caring about the response of the target systems. This type of attack is especially effective since the attack packets seem to be coming from different sources and thus the perpetrators are hard to trace.
Hackers using IP address spoofing frequently make use of randomly chosen IP addresses from the entire spectrum of IP address space while some more advanced hackers only use the unregistered portions of the IP address range. IP address spoofing, however, is less effective than using botnets for DoS attacks because it can be monitored by Internet authorities using backscatter technique which can determine a DoS attack based on the number of invalid IP addresses used in the attack. Nevertheless, it remains a viable alternative for hackers.
IP address spoofing is also a very useful tool in infiltrating networks and overcoming network security measures. This happens when IP address spoofers use a trusted IP address within the network and thus circumvent the need to provide a username or password to log in to the system. This sort of attack generally is based on a specific set of host controls (such as rhosts) that are configured insecurely.
IP Address Spoofing Defense
Ingress filtering or packet filtering the incoming traffic from outside the system using a technology is an effective way of defending against IP address spoofing since this technique can determine if packets are coming from inside or outside the system. Consequently, egress filtering can also block spoofed IP address packets from exiting the system and launching an attack on other networks.
Upper layer protocols such as the TCP or Transmission Control Protocol in which a sequence of numbers is used to established a secure connection with other systems is also an effective way of defending against IP address spoofing.
Turning off source routing (loose and strict) on your network routers can also assist in preventing hackers from taking advantage of many spoofing features. Source routing was a technology used widely in the past to prevent a single network fault from causing a major network outage, but the current routing protocols on the Internet today makes it all but unnecessary.


Follow Us!