RFC 2829 – Authentication Methods for LDAP defines the basic threats to an LDAP directory service:
- Unauthorized access to data via data-fetching operations,
- Unauthorized access to reusable client authentication information by monitoring others' access,
- Unauthorized access to data by monitoring others' access,
- Unauthorized modification of data,
- Unauthorized modification of configuration,
- Unauthorized or excessive use of resources (denial of service), and
- Spoofing of directory: Tricking a client into believing that information came from the directory when in fact it did not, either by modifying data in transit or misdirecting the client's connection.
Threats (1), (4), (5) and (6) are due to hostile clients. Threats (2), (3) and (7) are due to hostile agents on the path between client and server, or posing as a server.
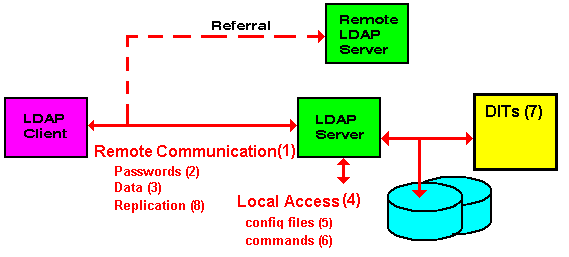
Protecting LDAP Security
RFC 2829 – Authentication Methods for LDAP also defines the mechanisms by which the LDAP protocol suite can be protected:
- Client authentication by means of the SASL mechanism set, possibly backed by the TLS credentials exchange mechanism,
- Client authorization by means of access control based on the requestor's authenticated identity,
- Data integrity protection by means of the TLS protocol or data-integrity SASL mechanisms,
- Protection against snooping by means of the TLS protocol or data-encrypting SASL mechanisms,
- Resource limitation by means of administrative limits on service controls, and
- Server authentication by means of the TLS protocol or SASL mechanism.
LDAP Authentication Types
LDAP v3 specifies three authentication types:
- No Authentication
- Basic Authentication
- Simple Authentication and Security Layer (SASL)
The use of "No Authentication" is acceptable when sharing public data.
Basic Authentication is similar to Basic Authentication under HTTP. Authentication is accomplished through the use of a DN (Distinguished Name) and a password. This data is sent either in plaintext or encoded using Base64 encoding.
SASL (Simple Authentication and Security Layer) is a framework for plugging in alternative security mechanisms. These security mechanisms include:
- Kerberos Version 4
- S/Key
- GSSAPI
- CRAM-MD5
- TLS
- ANONYMOUS

Follow Us!