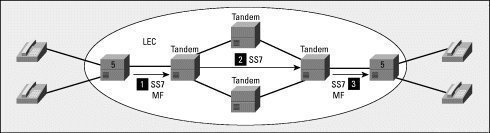
An LEC, or Local Exchange Carrier, is a telephone company that is responsible for managing calls within a specific territory, such as a city or county. The vast majority of the United States is managed by LECs, which differ from IXCs, or Interexchange Carriers. While LECs manage local calls between two parties, IXCs are responsible for managing long-distance calls between multiple LEC territories, known as LATAs, or Local Access and Transport Areas.
How LEC Works
An LEC manages all calls, equipment, and customer queries within its respective LATA, although most LECs control multiple LATAs. Generally, an LEC is a relatively small telecommunication company that manages a rural area outside of the area of a larger telecommunication company, such as a small town that is not within the nearest city’s limits. An LEC may own its own equipment or may lease the equipment of a larger telecommunications company, but is responsible for its own customers and equipment in either circumstance.
Applications
LECs are used to provide telecommunications access to subscribers in a rural area or LATA that is not governed by a larger telecommunications company. LECs are advantageous to these subscribers because they allow them to contact local residents and may do business with an IXC to provide their customers with long-distance calls as an additional service.
LEC Duties
LECs provide number portability according to the Commission’s requirements.
LECs have the duty not to impose any limitations or discriminatory conditions in resale of its services.
LECs have the duty to create reciprocal compensation in telecommunication transport and termination.
LECs also provide dialing parity to other providers and permit these providers to get nondiscriminatory access to operator services, telephone numbers, directory listing and directory assistance, without dialing delays.




JudeWS
LEC says address not valid for local wireless tower. What information should eb provided for LEC to validate the address or update their database?