The Lsass.exe System Error is a problem that may affect a computer system running Windows XP. Lsass (Local Security Authentication Subsystem Service) manages the log in process information for accounts on the system.
Three things that may cause an error with the Lsass.exe process:
- The msvcrt.dll file was corrupted or replaced with an incompatible version.
- The user deleted or corrupted the Lsass.exe file.
- A virus made changes to the Lsass.exe file.
Restoring the Original msvcrt File
The system user must have access to the installation CD for their Operating System. Most Windows XP systems come with an installation disk, while newer versions may not if the system was pre-installed and can be restored through the recovery partition of their drive and the recovery console.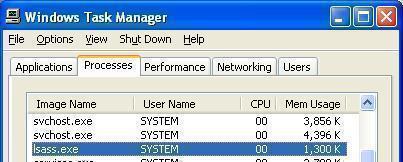
For those who have the installation media:
1) Insert the CD/DVD into system’s disc drive.
2) Restart the system while making sure that the BIOS is set to load the CD/DVD before attempting to load the hard disk. In some systems, there may be an option to choose which item is booted by entering the boot menu (usually on notebook PCs).
This will boot up the Windows Setup process from the disk.
Or
For those who have a recovery partition on their hard disk:
During the startup process, prior to booting into Windows, press the F11 button on the keyboard to tell the BIOS to load the recovery partition. In some systems, the key may be the “Ctrl” key or another option. Once the recovery partition has booted, the recovery options will be listed.
How to Restore msvcrt.dll from this point:
Through both the Installation media and the recovery partition, it is possible to access the recovery function at the “Welcome to Setup Screen” by pressing the letter “R” on the keyboard once.
This will open the restore command that allows the user to select from a list of possible installed Windows Operating Systems on the hard disk. Choose the option that is installed on the disk, which usually corresponds with the number “1,” but it can be other options depending on how the system is set up.
From this point, type in the administrator password (usually blank) then press “Enter” to continue.
Note: Depending on the system’s manufacturer, the user may need to use a special default administrator password instead of the one that is installed on the actual “Administrator” account. Check the computer manual or other reference materials if the default administrator password does not work.
This allows access to the recovery console, which looks very similar to a command prompt where commands can be typed in for the console to use. Type each of these commands and press the “Enter” key [ENTER] in the following order:
cd system32 [ENTER]
ren msvcrt.dll msvcrt.old [ENTER]
F: [ENTER]
cd \i386 [ENTER]
expand msvcrt.dl_ C:\windows\system32 [ENTER]
exit [ENTER]
Restart when complete.
Note: “F:” is the letter of the drive that the CD/DVD is being loaded from so it can vary from machine to machine. If running from the recovery partition, it is important to know the drive letter for the recovery partition for it to work (but in some cases the recovery partition is hidden and has no physical drive letter assigned to it).
A breakdown of what is happening:
The “cd system32” command is changing the directory “cd” to system32 on the Windows partition of the hard disk.
The “ren” command is to rename the file “msvcrt.dll” to “msvcrt.old“, in order to replace it with later commands. The msvcrt.dll file is actually the “Microsoft Visual C++ Runtime” library file, which has a specialized function “_resetstkoflw” that is used to recover from a stack overflow with Windows.
The “F:” or whichever drive letter the recovery is coming from accesses that drive.
The “cd\i386” command changes the directory to \i386
The “Expand msvcrt.dl_C:\windows\system32” command tells the recovery console to place the new msvcrt.dll file at the C:\windows\system32 directory.
The “exit” command exits the recovery console then asks the user to restart the machine.
If the msvcrt.dll file was causing the problems with the startup, then the machine should now successfully boot into Windows without the Lsass.exe error.
When Lsass.exe is Deleted, Corrupted, or Misplaced
Sometimes people unknowingly damage their Windows distribution by deleting, renaming, moving or corrupting the Lsass.exe file, even though Windows warns not to change documents contained in various folders. When this happens, the system may run like normal until it goes into sleep mode and resumes or the system is rebooted. The user is then greeted with a blank screen and an error is displayed about denied access or a missing Lsass.exe file.
The main problem that this causes is it restricts the system from loading into Windows completely, which reduces the ability to resolve the issue.
In this instance, it is best to use the restoration process outlined above for the msvcrt.dll to replace the missing Lsass.exe file.
Another option is to connect the affected hard drive to another system. This process is advanced and only someone with experience should do it as the system may get damaged.
Once the hard disk is attached to the new system, navigate to the file structure to where the Lsass.exe file is located. Most commonly, this is found in the “C:\Windows\System32” directory.
The user will then be able to copy the matching version of the Lsass.exe file from:
- The system that the hard disk was connected to (if the same version of Windows is available)
- A copy from the installation media for the Windows Version installed on the hard disk
- A correct version stored on external media
If the file was simply renamed or misplaced into another folder, the user can simply give the Lsass.exe file its original file name or replace it by moving it back into its original directory.
Once this process is complete, the user can then remove the hard disk safely (after the other computer has been shut down or the appropriate process to remove the disk has been fulfilled) then place it in the original computer that it was taken from. The system should then be able to successfully boot into Windows and allow the user to access the desktop once again.
Warning: The manual replacement of the Lsass.exe file via hard drive transplant should be a final measure and only someone who knows what they are doing should carry it out.
When a Virus Causes Lsass.exe Damage
An alternate method to combat this when signing onto Windows (not always possible when there is an Lsass.exe error) is to do the following:
Before the system is done booting and before the “Lsass.exe” program initiates, open the run dialog by either clicking the start button on the task bar then selecting run or holding down the “Windows” key and pressing the letter “R” for the shortcut to the dialog entry.
Enter the following phrase as a run command “shutdown-a” then press Enter or select the “ok” button to run the command.
Note: The “shutdown-a” command tells the computer to abort the shutdown procedure, which allows the user to continue with this remedy.
Once the computer connects to the Internet, navigate to the Microsoft Security Bulletin to update critical portions of the operating system that the virus affected. The security bulletin to look at is the MS04-11 (available at: MS04-11)
Download the file that is available in the list of options that corresponds with the Windows Operating system. Update the remote code execution controls on the machine to remedy the problem.
To apply the remedy to the computer, it is essential to have the correct security bulletin version. To install the update, open the resulting downloaded file from the download directory that it is in.
The update process will automatically continue once installation is authorized through the prompted messages.
Note: If the computer is not connected to the Internet, download the security bulletin update file onto a storage medium, which can then be executed from the computer once the shutdown abortion command has been run.
Once the security update is installed, ensure that a firewall is enabled and running correctly. This will help to prevent unauthorized access to the computer. Install an anti-virus service to help remove the virus and improve security.
Options to look into include:
Microsoft Security Essentials (Available at Microsoft)
AVG Antivirus Free Edition (Available at AVG Antivirus)
Malwarebytes Antimalware (Available at Malwarebytes)
Note: Update the anti-virus program to help rid the computer of viruses such as those that cause the Lsass.exe system error.
Last but not least, ensure that Windows is up to date. One of the best ways to do so is to run the system update service on the computer. In order to do this, visit the Microsoft Windows update site and follow the instructions that are provided. http://windowsupdate.microsoft.com/
If these options fail to fix the Lsass.exe error, try going through the steps once again to ensure that a crucial step was not missed. If the problem persists, ensure that a secondary source is not causing the problem.
Suggestions for Lsass.exe Virus Removal Include:
Booting in Safe Mode – Press the “F8” key during the startup sequence to show the extra boot options. Choose the “Load Windows in Safe Mode” option then use an anti-virus program or perform one of the fix options mentioned above to attempt to resolve the issue.
Restoring from System Restore – Another option is to use the system restore feature to put the system back to a state where the problem did not exist. This requires momentary access to the system. Type in the following then press enter to initiate the system restore console: %systemroot%\system32\restore\rstrui.exe
Follow the steps in the system restore console to restore the computer to a previous state where the problem did not exist. Once this is done, follow the steps above to update the computer operating system and secure it against similar problems for the future.
Note: In many cases, the Sasser worm or one of its many variants causes the Lsass.exe corruption. The Sasser worm can be halted with third party tools such as the Symantec removal tool, but patching of the system via updates and a thorough virus scan is necessary to ensure complete removal of the worm.
Download the Symantec Sasser Removal Tool at: Symantec

frederik
just suggest to try “Long Path Tool” program