Mirroring is the automated process of writing data to two drives simultaneously. Mirroring is used to provide redundancy, backup, multiple concurrent accesses and uninterrupted accessibility.
If one drive fails, the redundant drive will continue to store the data and provide access to it. The failed drive can then be replaced and the drive set can be re-mirrored. Disk data mirroring is also done for disaster recovery. Entire data is mirrored at remote sites which can then be used for recovery in case of disasters or breakdowns. Data mirroring can be achieved synchronously or asynchronously depending on the implemented mirroring technology.
Mirroring is used in RAID Level 1.
Software Mirroring vs. Hardware Mirroring
Disk mirroring can be implemented entirely in software. Software mirroring can be less expensive, but it is also slower. Software mirroring requires the host computer to write the mirrored data twice.
Disk mirroring can be implemented in hardware on the host I/O controller. The burden of writing each bit of data twice is placed upon the I/O controller, which is specifically designed for it.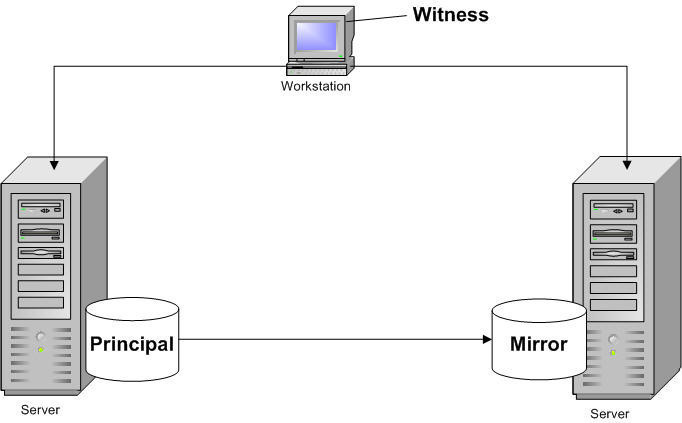
Disk mirroring can also be implemented in hardware on an external storage device, such as a RAID array. In this case, mirroring is completely removed from the host’s responsibility list.
Hot Swappable Hardware
If the hardware is hot swappable, it is possible to replace a failed disk without powering off the computer. You can take out the old drive and put in the new drive with no service outage.
If the hardware does not support hot-swap, you must schedule a service outage, shut down and power-off the system, and then replace the drive.
Mirroring vs. Duplexing
Mirroring is the technique of using redundant disks. Duplexing is mirroring, with the addition of redundant host I/O controllers.
If you are using mirroring and your host I/O controller fails, you will not be able to access your data until you replace the host I/O controller. With duplexing, your data will still be available through the redundant controller.
Benefits of Mirroring
- Provides backup and constant availability for restoration
- Aside from backup, it provides multiple concurrent access to the same data on separate disks, resulting into load balancing
- Load balancing can enhance performance to great extent



Follow Us!