A page fault is an error known as the “0x50 Stop Error,” which occurs when a computer’s RAM requests a page of memory from the page file and does not receive it. Because the RAM needs the page of memory to continue running its current tasks, the CPU is forced to dump all of its current processes and display a blue error screen known as the “Blue Screen of Death” or (BSOD).
Page File and Nonpaged Area
Page faults arise from a miscommunication between two critical parts of the RAM known as the “page file” and the “nonpaged area.” The page file is where the RAM keeps all of its pages of memory that include information for important tasks that must be carried out, but are not actively in use. Contrastingly, the nonpaged area is where the RAM keeps all of the processes it is currently running. When the RAM needs a page of memory for a process in the nonpaged area, it contacts the page file and requests that specific page.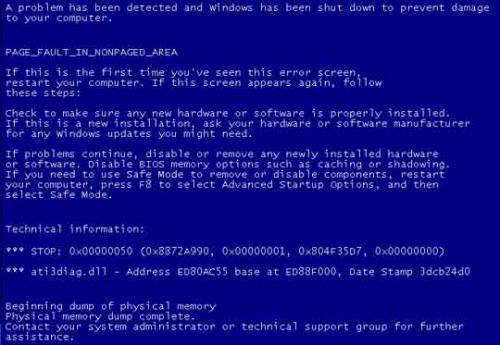
What Causes Page Faults
When the page file is unable to deliver a page of memory to the RAM’s nonpaged area, the CPU cannot process its current tasks. In order to prevent data loss or computer damage, the CPU stops running all processes and shuts the computer down. While software issues can cause page faults, problems with the user’s hardware, such as the RAM or hard drive, most commonly cause them.
How to Solve Page Fault In Nonpaged Area in Windows
If a software issue caused the page fault, the user should be able to simply reboot his/her computer and return to his/her previous tasks. If this does not work, the user may need to boot his/her computer in the last known good configuration from the boot screen or return the computer to a previous time with System Restore. If these methods do not work, the user should attempt to put his/her computer in safe mode and run the “chkdsk” command by opening the Start Menu, opening “Run,” entering “cmd,” and pressing OK. The user can then enter “chkdsk” and press the Enter key to make the computer run a scan of all hardware components in order to find any failures. If chkdsk returns any results, entering “chkdsk /f” will make chkdsk attempt to fix the errors. If this does not work, the user may need to replace his/her hard drive or RAM.

Melissa Adams
WOW! Excellent article. Thank you for describing this in such an easy way for non-techies to understand. Very helpful!
frederik
I suggest try to use “Long Path Tool” it is very helpfull
rejohn
Long Path Tool help me a lot when i have an issue like file deleting or
renaming the file. Also good to use if file name and file extension is
too long.