RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) is a wireless system used to identify tags. These tags may be attached to objects and even embedded under the skin of animals and human beings. Therefore, we can describe RFID as a form of identification tracking that allows retail outlets, airports, zoos, libraries, office buildings, warehouses, and different types of companies to locate and track property or people. For example, a retail store can use this system to locate any item and see on which shelf it is placed. Although there are other tracking methods, RFID is considered the most convenient and inexpensive tracking system.
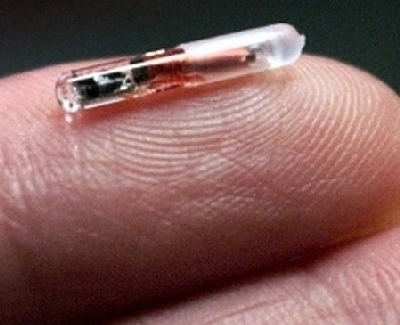
RFID Tags
RFID tags are devices used for Radio-frequency identification. A RFID tag consists of a microchip that is combined with an antenna or coil. The antenna picks up signals from an RFID reader and then returns the signal with additional information. The chip or integrated circuit is used to store the information that is collected from the signals picked up. The chip can also be used to process this information or to modulate and demodulate the tracked signal. However, some RFID tags are chipless. This means they do not use any integrated circuit to store information. Their advantage over traditional RFID tags is that they can be used in several different environments and are also less sensitive to temperature changes and radio frequency interference.
The size of a RFID tag can vary. It can be very small – like a grain of sand – or it can be as large as a small book. The RFID tag can be attached to a product, an animal or a human being for the purposes of identification.
RFID tags can either be active, passive or semi-passive. Active RFID tags require an internal power source to power the integrated circuit and then broadcast the response signal to the reader. The power source can be a replaceable battery or a sealed unit or can be connected to an external power source. Passive RFID tags do not contain an internal power source. When radio waves are encountered, an electrical current is induced in the antenna to form a magnetic field. This power is what is used to power up the passive RFID tag. Semi-passive RFID tags have their own internal power source which powers the chip but not the broadcasting of the signal. The response is powered when the energy is reflected back to the reader.
Passive RFID vs. Active RFID
Passive RFID tags operate using power from the RFID transceiver. Passive tags are small and inexpensive, but do not have good range.
Active RFID tags are usually powered by a battery. These tags are larger and more expensive, but offer a much better identification range.
Passive tags typically store between 32 and 128 bits of data, whereas active tags can store up to 1MB of data.
Passive tags are Read-Only; Active tags are typically rewritable.
How RFID Works
How RFID Transmitters Work
If RFID transmitters are used to track people, RFID tags are usually worn as bracelets or ID badges. RFID transmitters broadcast a continuous high frequency signal monitored by RFID readers.
How RFID Readers Work
RFID readers are receivers installed around a specific area every 100-200 feet in order to locate RFID transmitters or tags in the vicinity. Like other tracking technologies, RFID tracking relies on multiple receivers to determine an object’s location by calculating the distance between the RFID tag and each receiver, as well as the distance between receivers.
RFID Applications
RFID Tracking
RFID tracking refers to a more generalized use of RFID technology, in order to locate specific objects within a facility. RFID tracking is more popular than RFID security, although both can be used to locate various objects.
RFID Security
RFID security allows companies to perform a wide range of security related tasks by using RFID tags. For example, RFID security can be used in airports in order to locate personnel in case of an emergency and prevent unauthorized personnel from entering a restricted area. RFID security can also be used to locate specific individuals, before they exit a specific area. Likewise, RFID security can be used to identify individuals based on their names or ID numbers. RFID security is widely implemented in airports and other public places such as zoos, malls, and government facilities.
• RFID Personnel Badges
RFID personnel badges are used for identifying employees and controlling the access to restricted areas. Airports and amusement parks often use RFID badges to identify employees’ location and allow them to access specific areas.
• RFID Passports
RFID passports are similar to RFID badges. These are used in airports to quickly identify themselves without having to scan their passports into a computer or have airport personnel individually read them. RFID passports are convenient and provide encrypted security for both customers and employees. Likewise, RFID passports can be used to locate specific customers and flag customers who are not permitted to fly.
• RFID Baggage Tags
RFID baggage tags are similar to RFID passports but are pinned to customer luggage in order to quickly identify a customer’s property. Likewise, RFID baggage tags can be used to locate lost or stolen baggage in an airport and prevent theft. Additionally, RFID baggage tags can be used to inform customers where their baggage is stored on the plane and where it can be retrieved when the plane lands.
Advantages
RFID is advantageous because it is relatively easy to implement, cost effective, and does not interfere with the daily routine of customers and employees. RFID is an ideal method of preventing theft, tracking personnel, as well as locating specific items on demand.
Here are several advantages of RFID tags:
- No need for contact to operate.
- Does not require line of sight for communication.
- RFID tags can be read through a variety of substances such as the human body, snow, fog, ice, paint, and other conditions where barcodes would be useless.
- Fast processing even in challenging circumstances.
- It can be read at distances of 100 feet or more.
Disadvantages
Although RFID is advantageous, its ability to locate items is limited to a particular area. That is to say, albeit that RFID is ideal for locating items within a specific property, RFID is unable to track items that are further than 300 feet away.



Follow Us!