Troubleshooting VPN Services Overview
Troubleshooting VPNs typically encompass troubleshooting of the following configuration settings, or aspects of your remote access strategy:
-
IP connectivity.
-
Setting up of remote access connections
-
IPSec
-
IP routing
To create VPN connections, there are a few requirements that have to be met:
-
VPN services need to be enabled on the server.
-
VPN client software has to be installed on the VPN client. A VPN client utilizes the Internet, tunneling and TCP/IP protocols to establish a connection to the network
-
The server and client have to be on the same network.
-
A Public Key Infrastructure (PKI)
-
The VPN server and VPN client have to use the same:
-
Tunneling protocols
-
Authentication methods
-
Encryption methods.
-
-
Centralized accounting
A few really simple, basic elements that should be checked before you start any further troubleshooting approaches are listed below:
-
Verify that Routing and Remote Access service (RRAS) is enabled and configured on the VPN server.
-
Check whether the VPN server is configured to allow remote access. Access the Properties dialog box of the remote access server, and on the General tab, check whether the server is configured to enable remote access.
-
Check whether the VPN server is configured to allow VPN traffic.
-
Verify that the correct VPN protocol is enabled on the Ports Properties dialog box. In the Maximum Ports box, ensure that the number of VPN connections that the port type which you have selected can support; is configured to an appropriate value that can support your expected number of concurrent VPN connections.
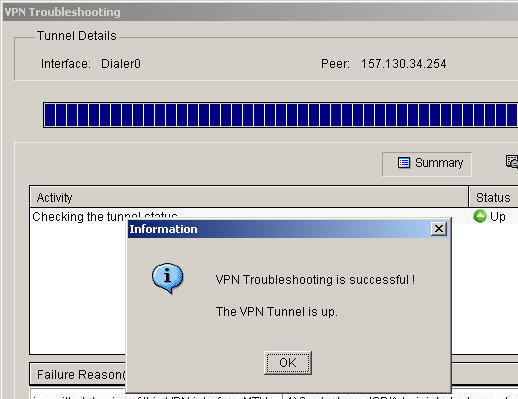
When is comes to troubleshooting why VPN connections cannot be established and why resources cannot be reached once the VPN connections are established, you may find that troubleshooting VPN connections and troubleshooting remote access connections have something in common. In addition, there may be numerous reasons why VPN clients cannot establish connections with the VPN service. Due to this, it may make sense to start your troubleshooting strategy by referencing the Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) reference model and then begin by checking the most simple connectively issues initially. You would proceed by moving up the OSI model, and troubleshooting the more intricate issues that could exist.
You should commence by verifying the underlying network connection, that is, verify that the client can establish the underlying connection to its ISP. When connecting to a VPN server through a persistent Internet connection, you should check that the VPN server has Internet connectivity. To check this, you can ping the VPN server to ensure Internet connectivity for the client and VPN server.
When testing Internet connectivity, check for the following:
-
Firewalls should be configured to allow the VPN connections.
-
Firewalls should not be blocking ICMP requests.
-
Any connection attempts should be to the proper IP address.
-
Check for any NAT configuration issues.
-
Check for any NAT translation issues.
After verifying connectivity between the client and VPN server, you should then start troubleshooting the more intricate issues:
-
Verify that the VPN server and client are set up to use the same VPN tunneling protocol to encapsulate data and manage VPN tunnels:
-
Both the VPN server and client should be configured to use Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol (PPTP) OR
-
The VPN server and client should be configured to use Layer Two Transport Protocol (L2TP).
Remember that Windows 95, Windows 98, Windows ME, Windows NT 4.0, Windows 2000, Windows XP and Windows Server 2003 support PPTP. Only Windows 2000, Windows XP and Windows Server 2003 support LTP.
-
-
Verify that the username and password being used is correct.
-
Verify that the VPN server and client are configured to use the same authentication protocol. A Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) is required for the mutual authentication of the VPN server and the VPN client. Certificates need to be installed on the VPN server and VPN clients. In addition to this, user authentication requires protocols such as Microsoft Challenge Handshake Authentication Protocol (MS-CHAP) and Extensible Authentication Protocol Transport Layer Security (EAP-TLS).
-
Verify that the VPN server and client are configured to use the same level of encryption, or encryption strength. The primary recommended levels of encryption are the Strong Encryption option (56-bit key is used for encryption), or the Strongest Encryption option (128-bit key is used for encryption).
-
Verify that no remote access policies are preventing the VPN connection from being established. Remember that all conditions in a remote access policy have to be matched for a remote access connection attempt to be allowed. When a user attempts to establish a connection, the remote access policies are evaluated to determine whether the user is permitted to access the remote access server. The user is only allowed access once all the conditions in the remote access policy allow access. In addition to this, if there are any policies that deny access, the connection will then be denied. When using remote access policies, the user account should be configured to use remote access policies. You can verify this on the Properties dialog box of the user account, on the Dial-in tab. The Control Access Through Remote Access Policy option should be enabled. If you are not using remote access policies, then the user has to be configured with dial-in permission on the Account Properties sheet (Dial-In tab).
Tools and Command-line Utilities for Troubleshooting VPN Connections
A few command-line utilities and methods which you can use when troubleshooting VPNs are listed here:
-
Event Viewer; can be used for viewing and analyzing logging information when audit logging is enabled.
-
IPCONFIG; for testing of basic IP configuration settings and local system configuration settings, including:
-
DNS server configuration settings.
-
WINS server configuration settings.
-
PPP adapter settings
-
WAN adapter settings
NBTSTAT; for troubleshooting of WINS and NetBIOS issues.
-
-
Netsh ras diagnostics; for enabling diagnostics capabilities for remote access connections.
-
NSLOOKUP; for intricate troubleshooting of DNS issues.
-
PING utility; for testing of connectivity.
You can use the Routing And Remote Access console to examine and manage remote access clients that have established connections to the remote access server.
To view the status of connected remote access clients,
-
Click Start, Administrative Tools, and then select Routing And Remote Access to open the Routing And Remote Access console.
-
In the console tree, select Remote Access Clients.
-
All currently connected remote access clients are displayed in the details pane of the Routing And Remote Access console.
-
Right-click the user name that you want to examine, and then select Status from the shortcut menu to view the status of the connection.
To disconnect remote access clients
-
Click Start, Administrative Tools, and then select Routing And Remote Access to open the Routing And Remote Access console.
-
In the console tree, select Remote Access Clients.
-
In the details pane, right-click the user name that you want to disconnect, and then select Disconnect from the shortcut menu
Troubleshooting VPN tunnels that cannot be Established
When you have a problem with establishment of the VPN tunnel, use the list below as a quick reference guide for troubleshooting this specific issue:
-
Ensure that the correct IP address is being used for the connection. If the incorrect address is being used, the PPTP session will reset.
-
Ensure that there are no packet filtering mechanisms between the VPN server and VPN client which could be preventing the connection from being established.
-
Check whether the packet filtering on any routers on the path are blocking any required protocols.
-
Check the configuration of the VPN tunneling protocols:
-
L2TP, UDP port 1701.
-
PPTP, TCP port 1723 & protocol ID 47 for control session and GRE.
-
IPSec, protocol ID 50 and 51 for IPSEC Authentication Header and IPSec Encapsulating Security Payload.
-
IP-IP, IP protocol ID 4.
-
Troubleshooting Remote Access VPN Connections
A few guidelines for troubleshooting remote access VPN connections are listed below:
-
Verify that Routing and Remote Access service (RRAS) is installed and enabled on the VPN server.
-
For a remote access connection to be established between the VPN server and remote access clients, the Remote Access Server option should be enabled on the General tab of the Properties dialog box of the remote access server. You can use the Routing And Remote Access management console to verify that the Remote Access Server option is enabled.
-
Use PING to verify that the IP address of the VPN server can be reached.
-
Verify that the correct VPN tunneling protocol is enabled on the Ports Properties dialog box. The selected tunneling protocol should be supported by the VPN server.
-
Use the Maximum Ports box to ensure that the number of connections for the port type which you have selected is set to the appropriate value to support your VPN connections. Check whether all ports are being used.
-
If necessary, increase the number of PPTP ports or L2TP ports to cater for more concurrent VPN connections.
-
Verify that the VPN tunneling protocol of the VPN client is supported by the VPN server.
-
Ensure that the settings of the remote access policy and the settings configured in the properties of the remote access server are not conflicting.
-
Check whether the settings of the profile of the matching remote access policy are conflicting with the configuration settings of the VPN server. When this situation arises, the VPN connection attempt is denied.
-
The VPN remote access connection must have the correct permissions for the connection to be established. You can verify the permissions specified for the connection by examining the remote access policies and the dial-in properties of the specific user account.
-
The remote access server, the remote access policy, and the VPN client should all be configured to minimally use one common authentication protocol.
-
If MS-CHAP v1 is the authentication protocol being used, ensure that the user password is not more than 14 characters.
-
The remote access server, the remote access policy, and the VPN client should all be configured to minimally use one common encryption strength. You can verify this information on the Security tab of the Dial-Up Connection Properties dialog box.
-
The VPN remote access connection must have the correct permissions for the connection to be established. You can verify the permissions specified for the connection by examining the remote access policies and the dial-in properties of the specific user account.
-
Verify that the credentials of the VPN client can be authenticated by the VPN server. This includes:
-
User name
-
Password
-
Domain name.
-
-
Check whether the LAN protocols utilized by the VPN client is actually supported for, and enabled for remote access.
-
If the remote access server assigns addresses to VPN clients from a predefined static address pool, ensure that the address pool can handle the required concurrent VPN client connections. All additional VPN connection attempts are denied if the VPN server cannot assign an IP address because all existing IP addresses are already being utilized.
-
If the remote access server assigns addresses to VPN clients through the DHCP server, ensure that the DHCP server's scope can handle the addresses needed by the remote access server.
Troubleshooting VPN Connections which are Allowed when they should be Denied/Rejected
If you want to specifically deny VPN connections, based on the denial of remote access permission for the VPN connection, then you must use either of the methods listed here:
-
In the User object, the remote access permission must be specified as Deny Access.
-
In the User object, the remote access permission must be specified as Control Access Through Remote Access Policy. The initial remote access policy which is a match to the VPN connection should be configured as Deny Remote Access Permission.
Therefore, when VPN connections are Allowed when they should be Denied/Rejected, you need to ensure that the settings defined for the particular VPN connection deny permission in the User object.
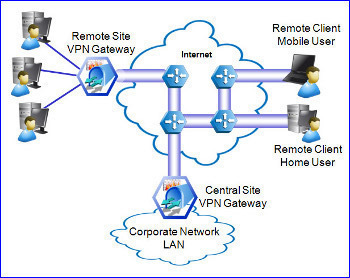
Troubleshooting Router-to-Router VPNs
A few guidelines for troubleshooting problems associated with router-to-router VPNs are summarized below:
-
The Router option and the LAN option should be enabled on the remote access server. You can verify this through the Routing And Remote Access console, by checking the configuration on the General tab of Server Properties dialog box.
-
Each remote access server should be configured to handle the appropriate number of connections. You need to verify that each server has the sufficient number of ports specified in the Ports node of the Routing And Remote Access console.
-
Each remote access server must have the Enable IP Routing option selected. Verify this by accessing the Routing And Remote Access console, and checking the setting of this option on the IP tab of Server Properties dialog box.
-
You have to ensure that the static routes are correctly configured on the remote access server for the traffic destined for the other network to be forwarded to the proper VPN router.
-
The VPN connection should have the proper permissions on the dial-in properties of the user account and in your remote access policies.
-
The settings specified in your remote access policies should not conflict with the remote access server's configured properties.
-
The demand-dial router, and answering remote access server and remote access policy should be using at least one common authentication method. They should also be using a common encryption level or strength.
-
The remote access server at each end of the connection has to be part of the RAS And IAS Servers group in the local domain.
Troubleshooting Resource Access Issues
When there is an issue with accessing resources past the VPN server, use the guidelines listed here:
-
The Entire Network option should be specified for the LAN protocols which are used by VPN clients.
-
When resources cannot be accessed, start by verifying that the IP address for the WAN or PPP Adaptor for the VPN client falls within the address range of the static IP address pool or within the range of the scope of the specified DHCP server. If applicable, check this for VPN routers as well.
-
If the VPN server uses a DHCP server for address assignment, and no DHCP server is available, the VPN server assigns addresses from the AutoNet address range (169.254.0.0/16). A route to 169.254.0.0/16, subnet mask 255.255.0.0 should be configured for the routers of the intranet.
-
If the VPN server assigns IP addresses through static IP address assignment, you have to ensure that the IP address range defined by the static IP address pool used by the VPN server can be accessed by hosts and routers. You can use static routing or a dynamic routing protocol such as RIP to define routes to the network.
-
In situations where the static IP address pool contains an IP address range that is actually a subset of the range of IP addresses for the network that the VPN server is connected to; the static IP address pool should not be allocated to any other TCP/IP nodes.
-
If the resources cannot be accessed when using their names, verify name resolution for the VPN connection:
-
For FQDN connectivity, ensure that the VPN client is able to access the specified DNS server.
-
For UNC connectivity, ensure that the VPN client is able to access the appropriate WINS server.
-
-
The issue could be due to a routing problem within the actual VPN connection. You should verify that the VPN routers have the proper route table entries for each remote network.

Follow Us!